

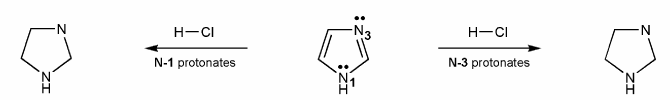
Imidazole (shown below) has two nitrogen atoms, N-1 and N-3. Which nitrogen is more basic?
To answer this problem, draw the product after each nitrogen protonates, and compare their stabilities. Explain your reasoning.
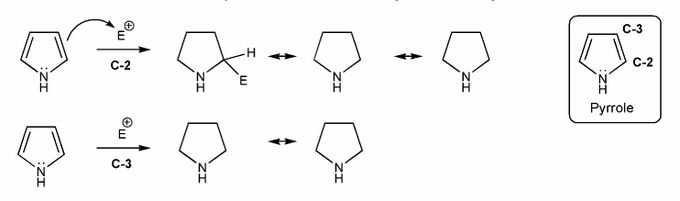
Pyrrole undergoes eletrophilic aromatic substitution at C-2. Let's compare the resonance forms of EAS carbocation intermediates to see why this is the case. What do you think? Why C-2 and not C-3?
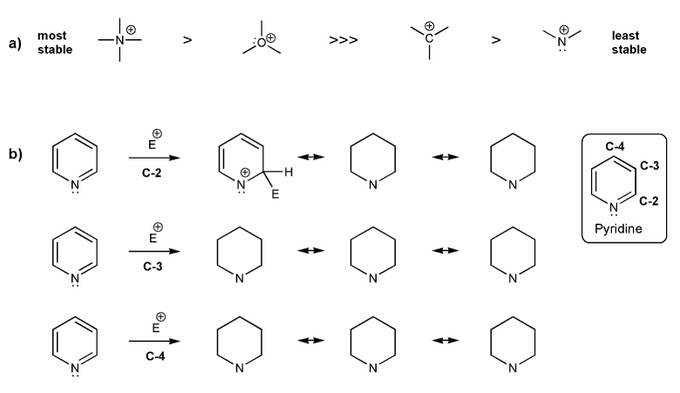
a) Rationalize the relative stabilities of the cation species below.
b) Pyridine undergoes eletrophilic substitution at C-3. Let's compare the resonance forms of EAS carbocation intermediates to see why this is the case. Consider part a) in your explanation.
The acyl group is a protecting group for amines. Amines can be acylated using acetic anhydride, and deacylated with base.
Propose a mechanism for each reaction.

Rank the amines A through D below in order of decreasing basicity (1 = most basic). Explain your reasoning.

Rank the amines W through Z below in order of decreasing basicity (1 = most basic). Explain your reasoning.

Show how each amine can be prepared from a carbonyl and an amine via reductive amination.

For each amine below, show all Hofmann elmination products.
If more than one product is formed, predict which one will be the major product.

Propose a synthesis to accomplish each transformation. The only carbon sources allowed are alkenes and NaCN.