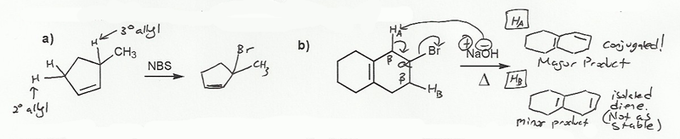
a) is a free-radical bromination. The radical will be formed at the most stable position, which will be the allylic position due to resonance (see problem 569). There are two allylic positions in this molecule, so the more substituted one will be the more stable; the bromine will add to the 3º allylic carbon.
b) is an E2 reaction. There are two types of beta protons and so two possible alkene products. One is an isolated diene and the other is a conjugated diene. Conjugated dienes are more stable, and so that will be the major product.