Textbook: Carey and Giuliano 8th Ed. (2010)
Chapter 4: Alcohols and Alkyl Halides
Practice Problems and Mendel Sets
Individual Problems
Mendel Sets
Textbook and Chapters: Carey and Giuliano 8th Ed. (2010), Chapters 4, 5
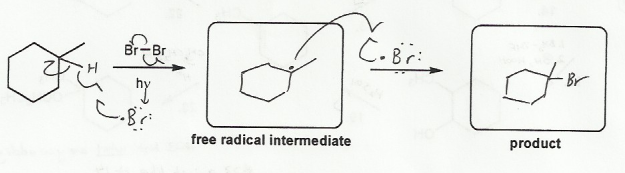
Keywords: carbocation rearrangement, free radical halogenation, mechanism
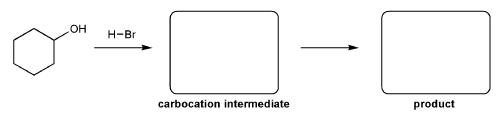
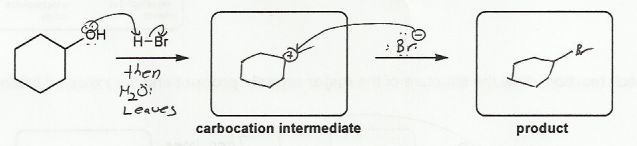
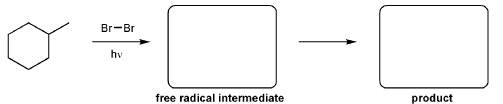
Description: Practice mechanisms from the first half of Fall semester orgo. Dehydration (E1), substitution with carbocation rearrangement (SN1), and free-radical bromination.
Total Problems: 3
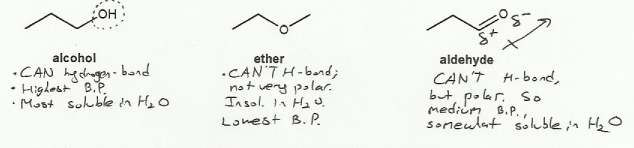
Textbook and Chapters: Carey and Giuliano 8th Ed. (2010), Chapters 4, 5, 6
Keywords: alkene addition, carbocation
Description: Identify the intermediates (carbocation, radical, borane intermediate, etc.) and products for important reactions dealing with alkenes. Good review for an orgo1 midterm.
Total Problems: 7
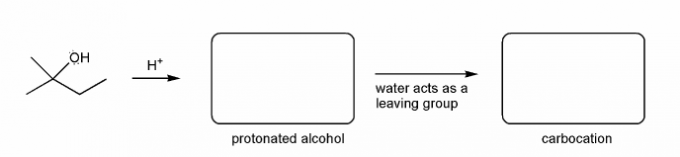
Textbook and Chapters: Carey and Giuliano 8th Ed. (2010), Chapters 4, 5, 6
Keywords: carbocation, carbocation formation, carbocation rearrangement
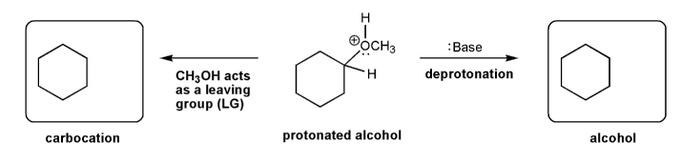
Description: This mendel set guides you through everything you have to know about carbocations:
- Ways carbocations form
- Carbocation rearrangements
- How carbocations react (elimination or nucleophilic attack)
Also includes some practice problems: addition to an alkene, dehydration (E1), and substitution (SN1).
Total Problems: 8