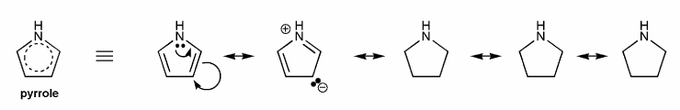
Pyrrole is an example of a heteroaromatic compound: it contains a heteroatom (atom that is not carbon or hydrogen, such as N, O, S, etc.), and is aromatic.
Because pyrrole is aromatic, we should be able to draw many resonance forms- usually as many resonance forms as sides (in this case, five sides, so five resonane forms).
Draw all resonance forms for pyrrole. (I've started you off.)