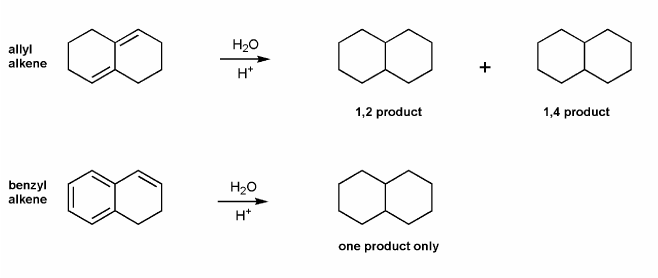
Draw all products for the two reactions below.
The allylic alkene gives two products- the 1,2 product, and the 1,4 product.
However, the benzylic alkene only gives the one product (analogous to the 1,2 product), instead of multiple products (like the 1,4 product, 1,6 product, and 1,8 product). Why is this the case?